bscan is a command-line utility to perform active information gathering and service enumeration. At its core, bscan asynchronously spawns processes of well-known scanning utilities, repurposing scan results into highlighted console output and a well-defined directory structure.
was written to be run on Kali Linux, but there is nothing inherently preventing it from running on any OS with the appropriate tools installed.
pip install bscan
Usage
bscan has a wide variety of configuration options which can be used to tune scans to your needs. Here’s a quick example:
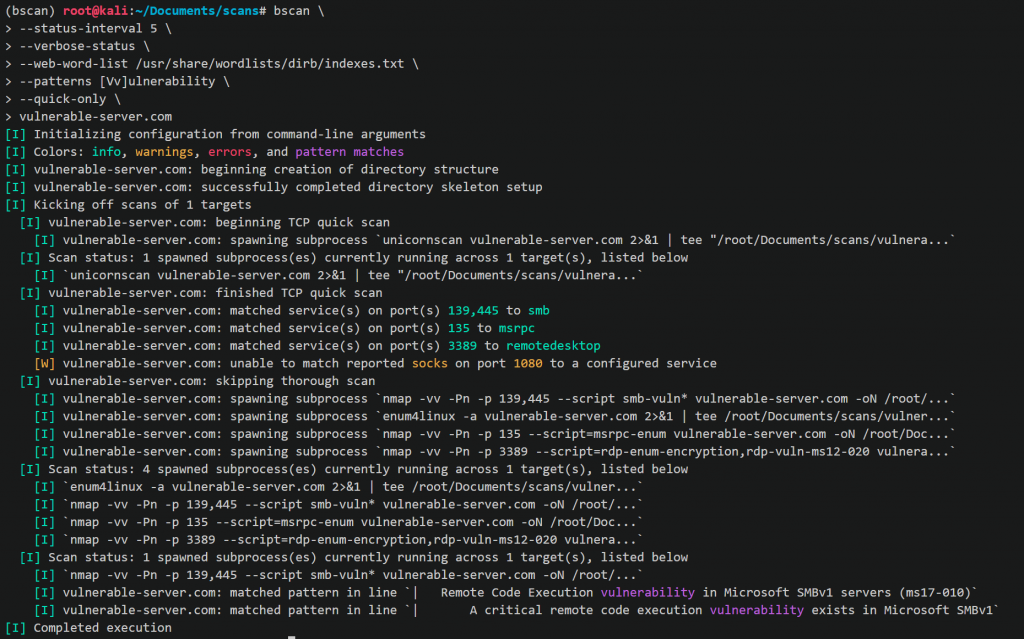
$ bscan \
> --max-concurrency 3 \
> --patterns [Mm]icrosoft \
> --status-interval 10 \
> --verbose-status \
> scanme.nmap.orgWhat’s going on here?
- –max-concurrency 3 means that no more than 3 concurrent scan subprocesses will be run at a time
- –patterns [Mm]icrosoft defines a custom regex pattern with which to highlight matches in the generated scan output
- –status-interval 10 tells bscan to print runtime status updates every 10 seconds
- –verbose-status means that each of these status updates will print details of all currently-running scan subprocesses
scanme.nmap.org is the host upon which we want to enumerate
bscan also relies on some additional configuration files. The default files can be found in the bscan/configuration directory and serve the following purposes:
patterns.txtspecifies the regex patterns to be highlighted in console output when matched with scan outputrequired-programs.txtspecifies the installed programs thatbscanplans on usingport-scans.tomldefines the port-discovering scans to be run on the target(s), as well as the regular expressions used to parse port numbers and service names from scan outputservice-scans.tomldefines the scans be run on the target(s) on a per-service basis
usage: bscan [OPTIONS] targets
_
| |__ ___ ___ __ _ _ __
| '_ \/ __|/ __/ _` | '_ \
| |_) \__ \ (__ (_| | | | |
|_.__/|___/\___\__,_|_| |_|
an asynchronous service enumeration tool
positional arguments:
targets the targets and/or networks on which to perform enumeration
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--brute-pass-list F filename of password list to use for brute-forcing
--brute-user-list F filename of user list to use for brute-forcing
--cmd-print-width I the maximum integer number of characters allowed when printing
the command used to spawn a running subprocess (defaults to 80)
--config-dir D the base directory from which to load the configuration files;
required configuration files missing from this directory will
instead be loaded from the default files shipped with this
program
--hard force overwrite of existing directories
--max-concurrency I maximum integer number of subprocesses permitted to be running
concurrently (defaults to 20)
--no-program-check disable checking the presence of required system programs
--no-file-check disable checking the presence of files such as configured
wordlists
--no-service-scans disable running scans on discovered services
--output-dir D the base directory in which to write output files
--patterns [ [ ...]] regex patterns to highlight in output text
--ping-sweep enable ping sweep filtering of hosts from a network range
before running more intensive scans
--quick-only whether to only run the quick scan (and not include the
thorough scan over all ports)
--qs-method S the method for performing the initial TCP port scan; must
correspond to a configured port scan
--status-interval I integer number of seconds to pause in between printing status
updates; a non-positive value disables updates (defaults to 30)
--ts-method S the method for performing the thorough TCP port scan; must
correspond to a configured port scan
--udp whether to run UDP scans
--udp-method S the method for performing the UDP port scan; must correspond
to a configured port scan
--verbose-status whether to print verbose runtime status updates, based on
frequency specified by `--status-interval` flag
--version program version
--web-word-list F the wordlist to use for scansCopyright (c) 2018 Brian Welch.
Source: https://github.com/welchbj/
![]()
